If you’re calculating your own depreciation, you may want to do something similar, and include it as a note on your balance sheet. (You can multiply it by 100 to see it as a percentage.) This is also called the straight line depreciation rate—the percentage of an asset you depreciate each year if you use the straight https://www.bookstime.com/ line method. However, note that eventually, we must switch from using the double declining method of depreciation in order for the salvage value assumption to be met. Since we’re multiplying by a fixed rate, there will continuously be some residual value left over, irrespective of how much time passes.
Do you already work with a financial advisor?
Instead, the asset will depreciate by the same amount; however, it will be expensed higher in the early years of its useful life. The depreciation expense will be lower in the later years compared to the straight-line depreciation method. HighRadius offers a cloud-based Record to Report Suite that helps accounting professionals streamline and automate the financial close process for businesses. We have helped accounting teams from around the globe with month-end closing, reconciliations, journal entry management, intercompany accounting, and financial reporting. FitBuilders estimates that the residual or salvage value at the end of the fixed asset’s life is $1,250.
When is the Double Declining Method used?

When the $80,000 is multiplied by 20% the result is $16,000 of depreciation for Year 2. The theory is that certain assets experience most of their usage, and lose most of their value, shortly after being acquired rather than evenly over a longer period of time. This method is often chosen when the asset’s value depreciates more rapidly in its early years, reflecting a more realistic depreciation pattern. We take monthly bookkeeping off your plate and deliver you your financial statements by the 15th or 20th of each month.
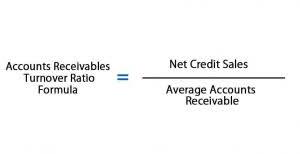
How to Calculate Straight Line Depreciation
- Business News Daily provides resources, advice and product reviews to drive business growth.
- Businesses choose to use the Double Declining Balance Method when they want to accurately reflect the asset’s wear and tear pattern over time.
- Download the free Excel double declining balance template to play with the numbers and calculate double declining balance depreciation expense on your own!
- A double-declining balance method is a form of an accelerated depreciation method in which the asset value is depreciated at twice the rate it is done in the straight-line method.
- Ask a question about your financial situation providing as much detail as possible.
- Tickmark, Inc. and its affiliates do not provide legal, tax or accounting advice.
The company will have less depreciation expense, resulting in a higher net income, and higher taxes paid. This method accelerates straight-line method by doubling the straight-line rate per year. The declining balance method is an accelerated depreciation system of recording larger depreciation expenses during the earlier years of an asset’s useful life. The system records smaller depreciation expenses during the asset’s later years.
How much will you need each month during retirement?
In summary, the choice of depreciation method depends on the nature of the asset and the company’s accounting and financial objectives. This process continues for each subsequent year, recalculating the depreciation expense based on the declining book value. As the asset’s book value decreases, the depreciation expense also decreases. However, using the double declining depreciation method, your depreciation would be double that of straight line depreciation.
Book value is the original cost of the asset minus accumulated depreciation. Both these figures are crucial in DDB calculations, as they influence the annual depreciation amount. To calculate the depreciation rate for the DDB method, typically, you double the straight-line depreciation rate. For instance, if an asset’s straight-line rate is 10%, the DDB rate would be 20%.

If something unforeseen happens down the line—a slow year, a sudden increase in expenses—you may wish you’d stuck to good old straight line depreciation. While double declining balance has its money-up-front appeal, that means your tax double declining balance method bill goes up in the future. When accountants use double declining appreciation, they track the accumulated depreciation—the total amount they’ve already appreciated—in their books, right beneath where the value of the asset is listed.

Even if the double declining method could be more appropriate for a company, i.e. its fixed assets drop off in value drastically over time, the straight-line depreciation method is far more prevalent in practice. Calculating the annual depreciation expense under DDB involves a few steps. First, determine the asset’s initial cost, its estimated salvage value at the end of its useful life, and its useful life span.